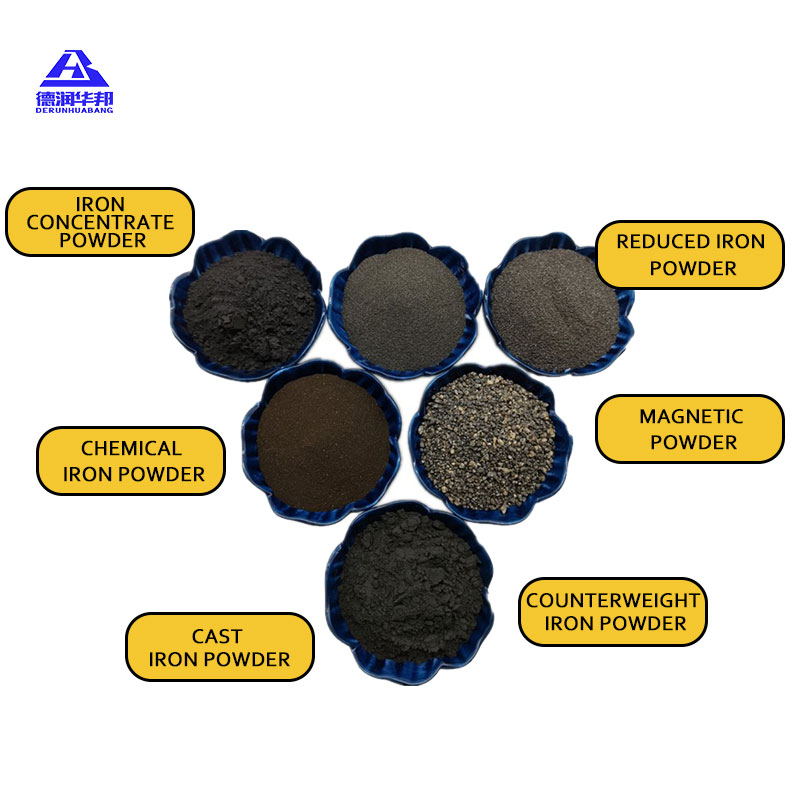
Iron powder has established itself as a cornerstone material in automotive parts manufacturing, playing a pivotal role in producing components that define performance, durability and reliability of vehicles. Its unique combination of moldability, strength and ability to enhance wear resistance makes it indispensable for crafting critical parts like engine components, transmission systems and steering gear. Moreover, as an additive in wear resistant materials, iron powder elevates longevity of automotive parts, addressing key challenges faced by automotive manufacturers and consumers alike. In an industry where every component’s performance directly impacts vehicle safety and efficiency, iron powder’s versatility and adaptability have made it a preferred choice across global automotive supply chains.
Engine manufacturing stands as one of the most demanding areas in automotive production, requiring materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, high pressure and constant friction. Iron powder rises to this challenge by serving as a primary material for numerous engine core components. One key application is in producing piston rings, which form a seal between pistons and cylinder walls to maintain compression and prevent oil leakage. Iron powder used for piston rings is processed to achieve a dense, uniform structure that resists wear even under repeated thermal expansion and contraction. Manufacturers blend iron powder with other elements to enhance its heat resistance, ensuring piston rings retain their shape and functionality over long periods of use. This not only improves engine efficiency by reducing energy loss but also minimizes maintenance needs by extending component lifespan.
Another critical engine component relying on iron powder is the valve seat insert. These inserts are mounted in cylinder heads to support intake and exhaust valves, enduring intense heat from combustion and repeated impacts from valve movements. Iron powder’s ability to be shaped into precise dimensions through powder metallurgy makes it ideal for this application. The powder metallurgy process involves compressing iron powder into the desired shape of the valve seat insert and then sintering it at high temperatures to form a solid, durable part. This process ensures the insert has a consistent grain structure, providing excellent heat dissipation and wear resistance. By using iron powder, manufacturers can produce valve seat inserts that fit tightly within cylinder heads, reducing noise and vibration while maintaining optimal engine performance.
Transmission systems, which transfer power from engines to wheels, depend heavily on components made with iron powder to handle high torque and continuous movement. Gear sets, the heart of transmission systems, are frequently manufactured using iron powder due to its ability to form complex tooth profiles with high precision. Iron powder gears are produced through powder metallurgy, a method that allows for intricate designs without the need for extensive machining. This not only reduces production time but also ensures each gear tooth has uniform strength, preventing premature failure under heavy loads. Additionally, iron powder’s natural density provides gears with the weight needed to maintain smooth engagement, reducing backlash and improving overall transmission efficiency.
Clutch plates, another vital transmission component, also benefit from iron powder’s properties. Clutch plates must withstand high friction when engaging and disengaging, requiring materials that are both wear resistant and heat tolerant. Iron powder is incorporated into clutch plate composites, where it acts as a reinforcement material to enhance structural integrity. The iron powder particles distribute evenly throughout the composite, creating a surface that resists abrasion and dissipates heat effectively. This ensures clutch plates maintain consistent performance even after repeated use, reducing the risk of slippage and extending the life of the transmission system.
Steering gear systems, which enable vehicle control, rely on iron powder to produce components that offer both strength and precision. Steering gears, such as rack-and-pinion gears, are often made using iron powder due to its ability to be formed into tight tolerances. The powder metallurgy process used to manufacture these gears ensures each tooth is accurately shaped, allowing for smooth and responsive steering. Iron powder’s strength also ensures steering gears can withstand the lateral forces exerted during vehicle operation, preventing bending or warping that could compromise handling.
Iron powder’s role as an additive in wear resistant materials further expands its value in automotive manufacturing. Many automotive parts, such as brake pads, brake rotors and suspension components, are exposed to constant friction and wear. By adding iron powder to the materials used for these parts, manufacturers can significantly enhance their durability. Iron powder particles act as a reinforcement, increasing the material’s hardness and resistance to abrasion. For example, brake pads containing iron powder maintain their thickness and friction properties longer than those without, reducing the frequency of replacements. Similarly, suspension components treated with iron powder-based coatings resist corrosion and wear, ensuring stable vehicle handling over time.
The use of iron powder in automotive parts manufacturing also offers economic benefits for manufacturers. The powder metallurgy process is highly efficient, producing minimal material waste compared to traditional machining methods. Iron powder can be recycled and reused in production, reducing raw material costs and environmental impact. Additionally, iron powder components require less post-production processing, shortening lead times and increasing production throughput. These advantages make iron powder a cost-effective choice for automotive manufacturers looking to improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
As automotive technology evolves, with a growing focus on electric and hybrid vehicles, iron powder’s role continues to adapt and expand. Electric vehicle motors, for instance, require high-strength, precision components that can withstand the demands of electric propulsion. Iron powder is well-suited for this application, as it can be used to produce motor cores and other parts that offer both strength and magnetic properties. Hybrid vehicle transmission systems also benefit from iron powder components, which provide the durability needed to handle both electric and internal combustion power sources.
Post time: Dec-10-2025